Government is all about Controlling | Governance is all about facilitations | There are Distinct Roles to play in Shaping Society | Global TV
The terms “government” and “governance” are often used interchangeably, but they represent distinct concepts crucial to understanding how societies function. Government refers to the formal institutions and officials, elected and appointed, responsible for making and implementing decisions. Governance, on the other hand, is a broader concept that includes the various ways through which societal interests are articulated and pursued, often extending beyond the formal mechanisms of government.
While government involves the official decision-making bodies, effective governance relies heavily on the active participation of citizens, activism, and civil society initiatives. This broader perspective of governance can bring significant benefits to a society, even when the government is performing poorly or is corrupt. It’s akin to a powerful flood overwhelming a small river or stream; the collective force of engaged citizens can drive substantial change.

The Power of Democracy: Beyond Government
Democracy is fundamentally about empowering people beyond the constraints of government structures. Derived from the Greek words “demos” (people) and “kratos” (rule), democracy signifies the rule of the people. This system champions individual rights and participation, ensuring that diverse voices are heard and that decisions reflect the collective will. In a robust democracy, the role of government is not just administrative but also as a conduit for the people’s aspirations and needs.
However, democracy’s true strength lies beyond formal governance. It thrives on citizen engagement, civil society, and grassroots movements that shape societal trajectories. This active participation allows individuals to hold the government accountable, scrutinize its actions, and advocate for policies that uphold justice, equality, and the rule of law.
Fundamental Pillars of Democratic Governance
Freedom of Expression:
Essential for democracy, this allows citizens to voice opinions, critique policies, and engage in public discourse without fear. It fosters innovation, dialogue, and informed decision-making, addressing complex societal challenges through diverse perspectives.
Inclusivity and Equality:
Democracy ensures marginalized communities and minority groups have a voice. By promoting dialogue and consensus-building, it enhances social cohesion and reduces the risk of polarization and conflict.
Active Participation:
Democracy involves more than voting. Citizen journalism, advocacy, and community organizing are crucial for influencing public opinion and holding power accountable, protecting against tyranny and oppression.

Challenges and Resilience of Democracy
Despite its strengths, democracy faces challenges like erosion of civil liberties, electoral manipulation, and institutionalized corruption. Disinformation and polarization further threaten democratic fabric by undermining trust in institutions. However, democracy’s resilience lies in its adaptability. By nurturing civic engagement, fostering transparency, and promoting inclusive decision-making, societies can harness democracy’s transformative potential for a just, equitable, and sustainable future.
Governance Begins with Self-Governance
Governance starts with self-governance as individual responsibility, discipline, and ethical behavior. This foundation is critical for a healthy democracy, fostering accountability and proactive citizenship.
Self-Governance: Pillars of Democratic Society
Personal Responsibility:
Encourages integrity and accountability, creating a ripple effect of ethical behavior and trust within the community.
Informed Decision-Making:
Empowers individuals to critically evaluate policies, participate in debates, and make informed choices reflecting societal best interests.
Empowerment and Initiative:
Leads to positive community contributions and the emergence of grassroots leaders driving social and economic progress.
Self-Induced Leadership Initiatives
When individuals recognize their potential for change, they often step into leadership roles, creating beneficial initiatives for their communities. These grassroots movements are crucial for:
Community Engagement:
Addressing needs through localized approaches ensures tailored solutions for specific community challenges.
Innovation and Creativity:
Grassroots initiatives bring fresh perspectives and innovative solutions, driving economic growth and social development.
Social Cohesion and Resilience:
Collective efforts foster unity and purpose, enhancing community resilience to various shocks.
Interplay Between Governance and Democracy
The vibrancy of democracy depends on citizen engagement and initiative. A vibrant democracy features:
Active Participation:
Citizens involved in civic life contribute to a responsive democratic system.
Diverse Voices:
Ensuring all voices are heard strengthens governance legitimacy and effectiveness.
Economic Vitality:
Grassroots initiatives stimulate economic activity and create jobs, enhancing overall vitality.
Accountability and Transparency:
Engaged citizens hold governments accountable, rooting out corruption and ensuring effective use of public resources.
Synergy of Governance and Democracy
Governance, starting with self-governance, expands through leadership initiatives. Active citizen participation is crucial for a vibrant democracy and economy. By taking personal responsibility, engaging in community initiatives, and advocating for inclusive governance, individuals drive meaningful change, contributing to a prosperous and equitable society. Democracy’s power lies not only in elected officials but in the collective actions of citizens, shaping the future of communities and nations.
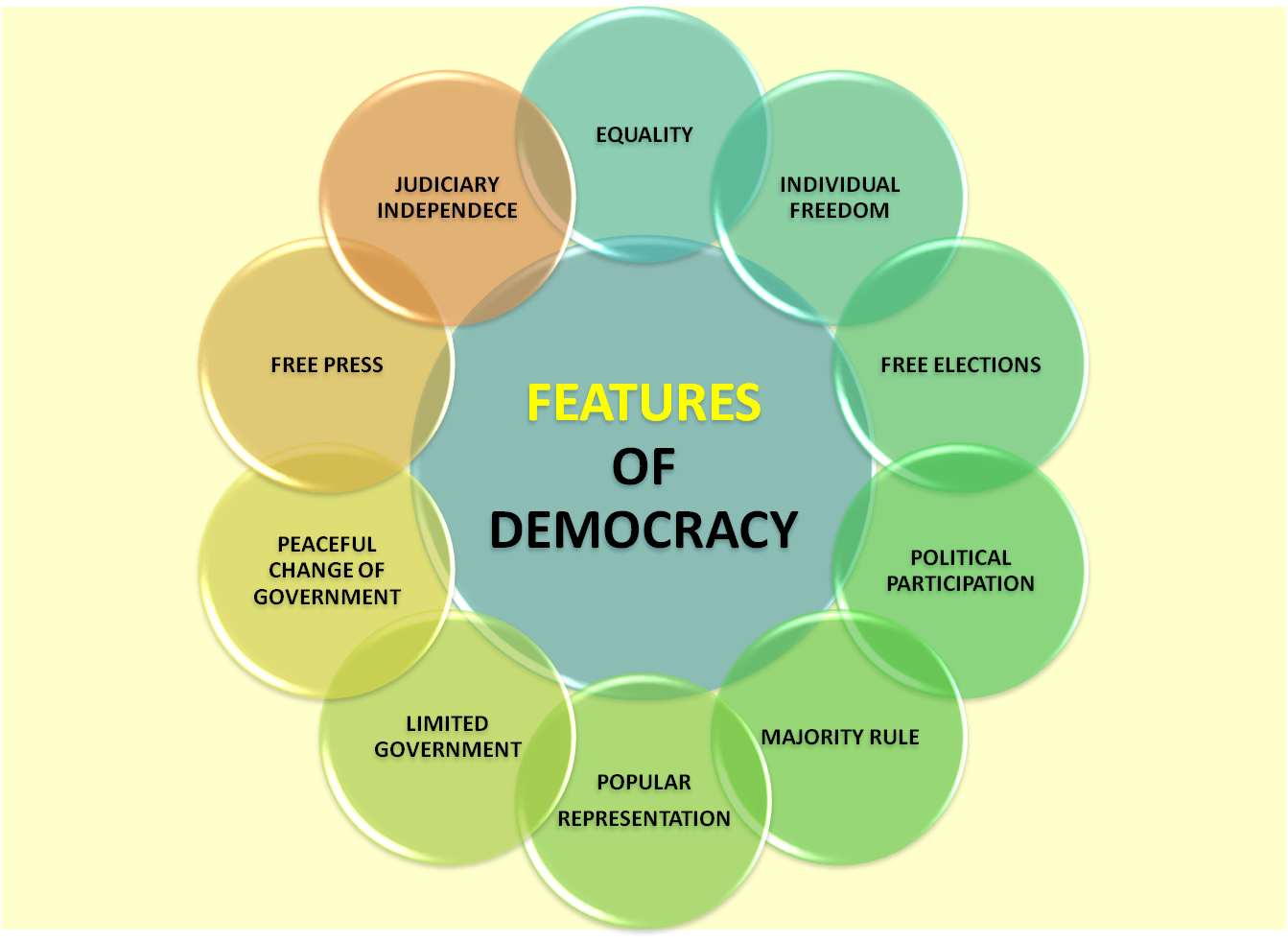
In Summary:
At the heart of effective governance lies the bedrock of democracy, where the power vested in the people catalyzes transformative change and ensures accountability even in the face of poor-performing or corrupt governments. One of the fundamental pillars of democratic governance is the freedom of expression, which allows citizens to voice their opinions, critique government policies, and participate in public discourse without fear of reprisal. This freedom serves as a catalyst for innovation, dialogue, and informed decision-making, fostering an environment where diverse perspectives can coalesce to address complex societal challenges.
Moreover, democracy thrives on the principles of inclusivity and equality, ensuring that marginalized communities and minority groups have a seat at the table. By fostering dialogue and consensus-building across different segments of society, democracy promotes social cohesion and resilience, mitigating the risk of polarization and conflict.
Importantly, the power of democracy is not confined to the ballot box but permeates every facet of society. Through mechanisms such as citizen journalism, advocacy campaigns, and community organizing, individuals can exert influence, shape public opinion, and hold power to account. In this way, democracy serves as a bulwark against tyranny and oppression, safeguarding fundamental rights and liberties.
However, the efficacy of democracy is not immune to challenges. In many parts of the world, democratic institutions face threats ranging from erosion of civil liberties to electoral manipulation and institutionalized corruption. Moreover, the rise of disinformation and polarization poses existential threats to the fabric of democratic societies, undermining trust in institutions and sowing discord among citizens.
Nevertheless, the resilience of democracy lies in its ability to adapt and evolve in response to changing circumstances. By nurturing a culture of civic engagement, fostering transparency and accountability, and promoting inclusive decision-making processes, societies can harness the transformative potential of democracy to build a more just, equitable, and sustainable future for all.
The power of democracy transcends the confines of government, permeating every aspect of governance and societal life. By empowering individuals, fostering dialogue, and upholding the principles of justice and equality, democracy serves as a beacon of hope, guiding humanity towards a brighter and more prosperous tomorrow.





